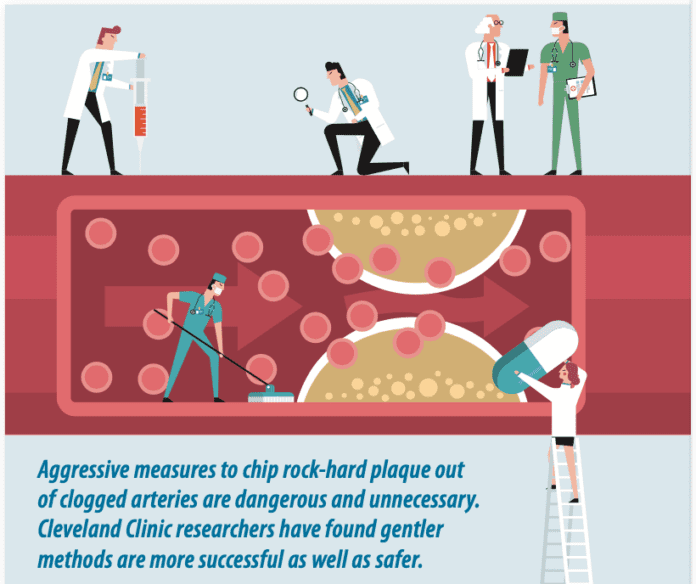
About 30% of patients with stable coronary artery disease have a totally blocked coronary artery, a condition known as a chronic total occlusion (CTO). CTOs arise from stable, slow-growing plaques that gradually narrow the interior channel of the blood vessel, reducing the volume of blood that can pass through. Over time, these plaques calcify and harden. When blood flow becomes totally blocked, angina can be debilitating.
To continue reading this article or issue you must be a paid subscriber. Sign in
Subscribe to Heart Advisor
Get the next year of Heart Advisor for just $20. And access all of our online content - over 2,000 articles - free of charge.
Subscribe today and save 38%. It's like getting 5 months FREE!